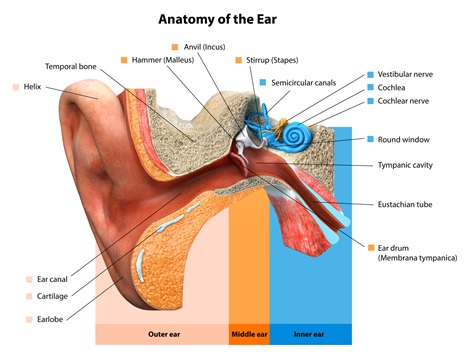
Ear infections happen when there is inflammation— usually from trapped bacteria—in the middle ear, the part of the ear connects to the back of the nose and throat. The most common type of ear infection is otitis media, which results when fluid builds up behind the eardrum and parts of the middle ear become infected and swollen.
If your child has a sore throat, cold, or an upper respiratory infection, bacteria can spread to the middle ear through the eustachian tubes (the channels that connect the middle ear to the throat). In response to the infection, fluid builds up behind the eardrum.
Children are more likely to suffer from ear infections than adults for two reasons:
- Their immune systems are underdeveloped and less equipped to fight off infections.
- Their eustachian tubes are smaller and more horizontal, which makes it more difficult for fluid to drain out of the ear.
“In some cases, fluid remains trapped in the middle ear for a long time, or returns repeatedly, even when there’s no infection,”
Leave a Reply