We will now consider the situation when we are given two sides and one angle of a triangle.
Ambiguous Case
If you are given two sides and a non-included acute angle and the side facing the given angle is less than the other side, you would obtain two sets of answers. The solution is said to be ambiguous.
Example:
Solve triangle PQR in which ∠ P = 56°, p = 10 cm and q = 12 cm
Solution:
Notice that we can construct two different triangles from the given information.
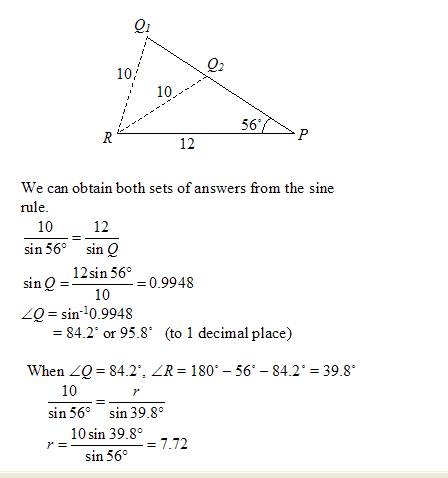
When ∠ Q = 95.8˚, ∠ R = 180˚ – 56˚ – 95.8˚ = 28.2˚
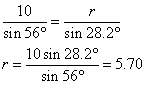
The two sets of solutions are:
∠ Q = 84.2°, ∠ R = 39.8°, r = 7.72 cm
∠ Q = 95.8°, ∠ R = 28.2°, r = 5.70 cm
Leave a Reply