In these lessons, we will learn:
- the Law of Cosines
- how to use the Law of Cosines when given two sides and an included angle
- how to use the Law of Cosines when given three sides
- how to proof the Law of Cosines
- how to solve applications or word problems using the Law of Cosine
Law of Cosines
The Law of Cosines relates the lengths of the sides of a triangle with the cosine of one of its angles.
The Law of Cosines is also sometimes called the Cosine Rule or Cosine Formula.
If we are given two sides and an included angle (SAS) or three sides (SSS) then we can use the Law of Cosines to solve the triangle i.e. to find all the unknown sides and angles.
We can use the Law of Sines to solve triangles when we are given two angles and a side (AAS or ASA) or two sides and a non-included angle (SSA).
The Law of Cosines, for any triangle ABC is
a2 = b2 + c 2 – 2bccos A
b2 = a2 + c 2 – 2ac cos B
c2 = a2 + b 2 – 2ab cos C
The following diagram shows the Law of Cosines. Scroll down the page if you need more examples and solutions on how to use the Law of Cosines and how to proof the Law of Cosines.
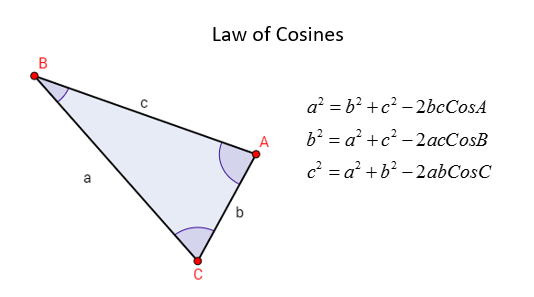
Law of Cosines: Given two sides and an included-angle
Example:
Solve triangle PQR in which p = 6.5 cm, q = 7.4 cm and ∠R = 58°.
Solution: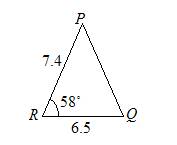
Using the Cosine rule,
r2 = p2 + q2– 2pq cos R
r2 = (6.5)2 + (7.4)2 – 2(6.5)(7.4) cos58°
= 46.03
r = 6.78 cm
Using the Sine rule,

∠Q = 180° – 58° – 54.39°
= 67.61°
∠P = 54.39°, ∠Q = 67.61° and r = 6.78 cm
Leave a Reply