We will first consider the situation when we are given 2 angles and one side of a triangle.
Example:
Solve triangle PQR in which ∠P = 63.5° and ∠Q = 51.2° and r = 6.3 cm. 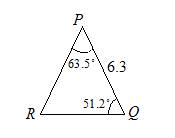
Solution:
First, calculate the third angle.
∠ R = 180° – 63.5° – 51.2° = 65.3°
Next, calculate the sides.

∠ R = 65.3°, p = 6.21 cm and q = 5.40 cm
Law of Sines: Given Two Sides And An Obtuse Angle
We will now consider the situation when we are given two sides and an obtuse angle of a triangle.
Example:
Solve ∆ PQR in which ∠ P =116°, p = 8.3 cm and q = 5.4 cm.
Solution: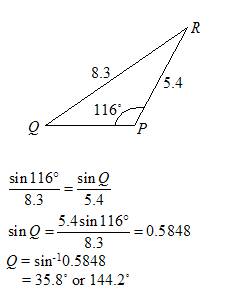
Q cannot be an obtuse angle because the sum of angles in the triangle will exceed 180˚. The only valid value for Q is 35.8˚.
∠ Q = 35.8°, ∠ R = 180° – 116° – 35.8° = 28.2°
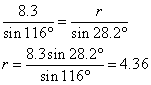
The solution is ∠ Q = 35.8° , ∠ R = 28.2° and r = 4.36 cm
Leave a Reply