In these lessons, we will learn
- how Trigonometric Graphs can be transformed
- the amplitude and vertical shift of Trigonometric Graphs
- the period and phase shift of Trigonometric Graphs
The following diagrams show how to determine the transformation of a Trigonometric Graph from its equation. Scroll down the page for more examples and solutions.
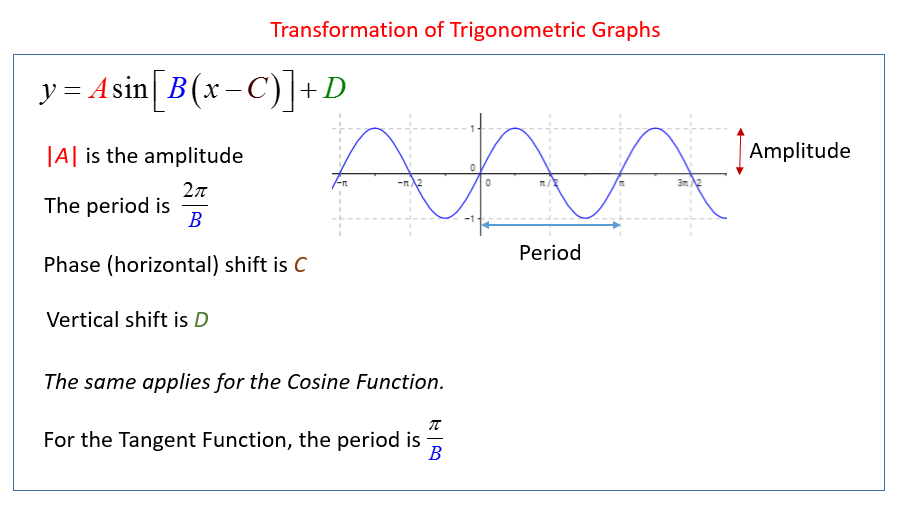
Amplitude Of Trigonometric Functions
The amplitude of a trigonometric function is the maximum displacement on the graph of that function.
In the case of sin and cos functions, this value is the leading coefficient of the function.
If y = A sin x, then the amplitude is |A|.
In the case of tan, cot, sec, and csc, the amplitude would be infinitely large regardless of the value of A. However, for a limited domain, the value of A would determine the maximum height of these functions.
Period of Trigonometric Function
The period of a function is the displacement of x at which the graph of the function begins to repeat.
Consider y = sin x
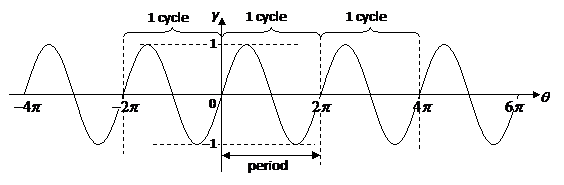
The value x = 2π is the point at which the graph begins to repeat that of the first quadrant. The coefficient of x is the constant that determine the period.
The general form is y = A sin Bx where |A| is the amplitude and B determines the period.
For the functions sin, cos, sec and csc, the period is found by P = 2π/B
Example:
Find the period of the graph y = sin 2x and sketch the graph of y = sin 2x for 0 ≤ 2x ≤ π.
Solution:
Since B = 2, the period is P = 2π/B = 2π/2 = π

Phase Shift of Trigonometric Functions
The general form for the equation of the sine trigonometric function is
y = A sin B(x + C)
where A is the amplitude, the period is calculated by the constant B, and C is the phase shift.
The graph y = sin x may be moved or shifted to the left or to the right. If C is positive, the shift is to the left; if C is negative the shift is to the right.
A similar general form can be obtained for the other trigonometric functions.
Example:
Find the amplitude, period and phase shift of
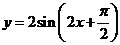
Solution:
Rewrite
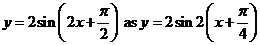
The amplitude is 2, the period is π and the phase shift is π/4 units to the left.
Basic Sine Function
Periodic Functions Definition, Period, Phase Shift, Amplitude, Vertical Shift.
A periodic function is a function whose graph repeats itself identically from left to right.
The period of a function is the horizontal distance required for a complete cycle.
The period of a basic sine and cosine function is 2π.
The frequency of a function is the reciprocal of the period.
The phase shift of a function is the horizontal shift of a periodic function.
The amplitude of a function is half the distance between the maximum and minimum values of a periodic function. The amplitude is always positive.
The vertical shift of a function is the vertical shift of a periodic function along the y-axis.
Leave a Reply